How to Optimize Your Wi-Fi Network at Home for Wireless Laptops, Desktops, iPads, and Tablets
Understanding Your Wi-Fi Network
To optimize your Wi-Fi network at home, it is essential to understand the fundamental aspects of Wi-Fi technology. Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11ac and 802.11n, play a crucial role in determining the speed and range of your network. The 802.11ac standard, for instance, offers faster speeds and better performance over longer distances compared to its predecessor, 802.11n. Knowing the capabilities of your Wi-Fi standard can help you make informed decisions about upgrading your hardware to enhance network performance.
Bandwidth and frequency bands are also critical factors in optimizing your Wi-Fi network. The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands each have their advantages and limitations. The 2.4 GHz band covers a larger area and penetrates walls more effectively but is more susceptible to interference from other electronic devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones. On the other hand, the 5 GHz band offers higher speeds and less interference but has a shorter range. Balancing the use of these frequency bands can significantly improve your network’s efficiency.
Router placement is another crucial aspect to consider. Positioning your router centrally within your home can help ensure an even distribution of the Wi-Fi signal. Avoid placing the router near thick walls, metal objects, or electronic devices that may cause interference. Elevating the router can also enhance signal coverage across multiple floors.
To further optimize your home network, it’s important to be aware of physical obstructions and potential sources of interference. Identifying and mitigating these factors can lead to a more stable and efficient Wi-Fi connection. Additionally, various tools and apps are available to analyze your current network’s performance. These tools can measure signal strength, identify dead zones, and suggest areas for improvement. By leveraging these resources, you can gain valuable insights into optimizing your home Wi-Fi network for all your wireless devices.
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach happens when sensitive information is accessed or disclosed without authorization….
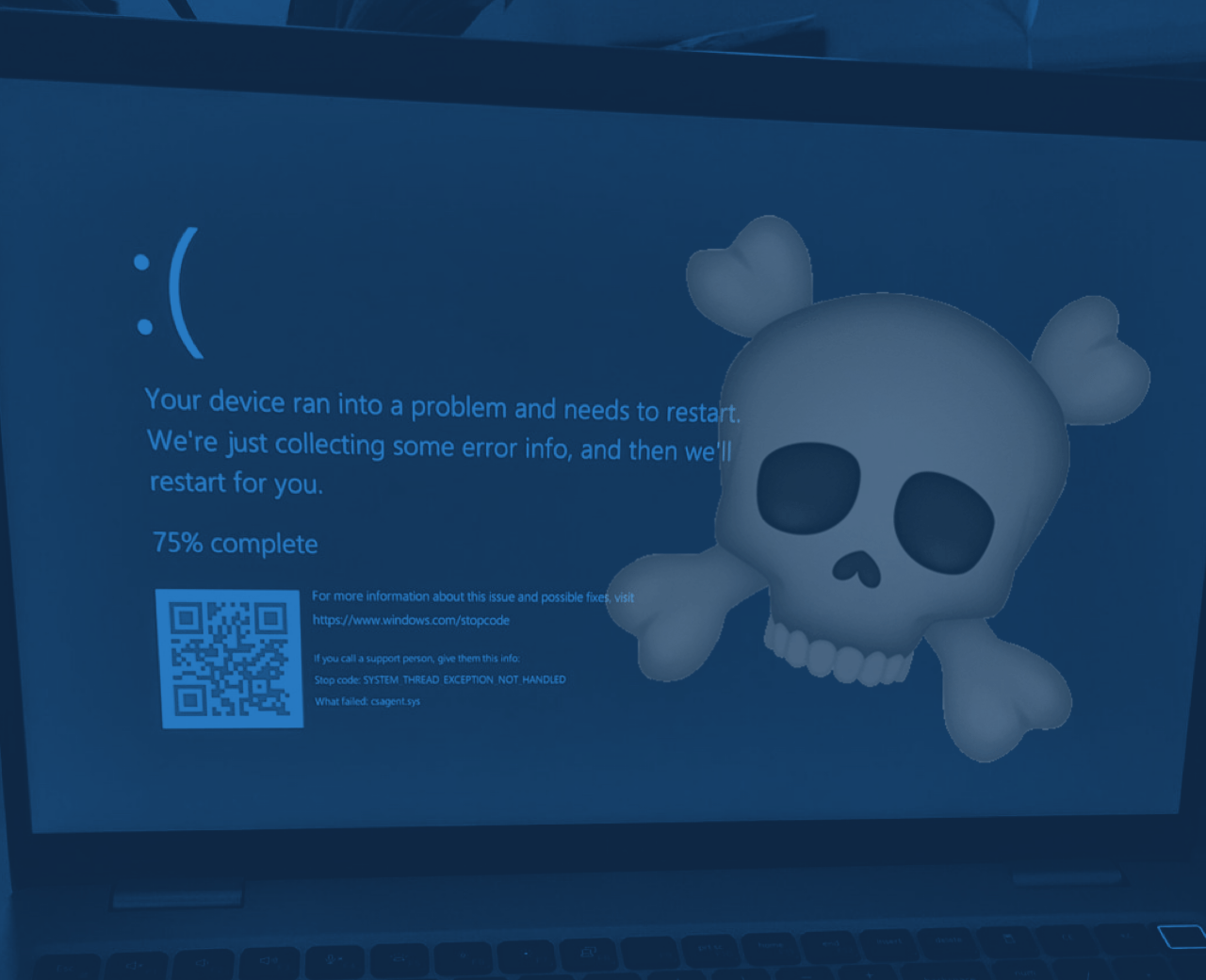
The Microsoft Outages 2024: What is CrowdStrike?
Learn about CrowdStrike its role in the cybersecurity industry and the latest updates on the Microsoft Outages…
The Microsoft Outages: Impact on Flights, Companies, and Services Worldwide
The recent Windows outages that have disrupted various sectors globally, affecting industries such as aviation, healthcare, and corporate environments….
Top 10 VPN Services for 2024: The Ultimate Guide
The best VPN services for 2024, including ProtonVPN, NordVPN, Surfshark, and more. From top-tier security, streaming capabilities to user-friendly interfaces…
The ‘Port Shadow’ Flaw: Which VPN Providers Are Safe Now?
The port shadow vulnerability highlights the risks associated with sharing a VPN server with other users, potentially leading to privacy…
Transforming an Old Laptop into a Chromebook: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to transform your old laptop into a Chromebook.Extend the lifespan of your aging laptop and enjoy a smooth…
Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence in Education
Adaptive learning platforms, supports by AI, are revolutionizing the educational sector. However, the growing presence of AI in education is…
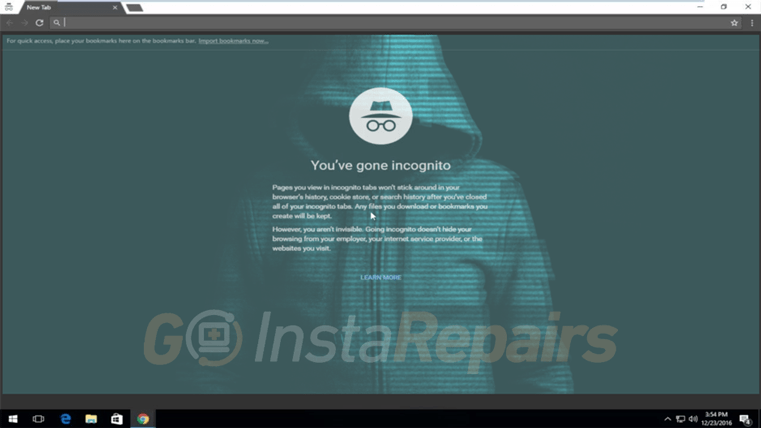
Is Google Chrome’s Incognito Mode Actually Private?
Discover the true capabilities and limitations of Google Chrome’s Incognito Mode. Learn how it protects your local browsing history but…
My Computer Has Been Hacked
Secure and protect your system for both Windows and macOS platforms. Stay vigilant and proactive to safeguard your computer and…
Poseidon Mac Stealer Distributed via Google Ads: A New Threat
Poseidon Mac Stealer. Distributed through deceptive Google Ads, this sophisticated malware infiltrates systems to exfiltrate sensitive information….
Network Basics to Keep Your Computer Secure (Easy and Simple
Learn what is an IP address, the importance of DNS translating domain names (or website URLs) to IP addresses,…
Guide to Troubleshooting Paper-Jam in your Printer
From proper paper loading and using the correct paper type to regular maintenance and understanding environmental factors to keep your…
Different Types of Rootkits
Learn about the different types of rootkits, including user mode, kernel mode, and firmware rootkits, and understand their operating mechanisms…
What is a Rootkit?
Although most rootkits affect the software and the operating system, some can also infect your computer’s hardware and firmware. Rootkits…
How to Remove a User from a Shared Windows Device
Learn how to manage and remove user accounts on Windows 10 and 11 to enhance security, free up space, and…
Most Common Symptoms That Your Computer is Infected with Malware
Discover the critical symptoms of malware infections, from on-screen warnings and browser behavior changes to performance issues and suspicious activities…..
Top 5 Smart Security Cameras for Your Home Recommended by
The top 5 smart 4k security cameras for home surveillance. Reviews by, Lorex Technology and Goinsta Repairs, experts…
Microsoft’s New AI Feature will record everything! Your passwords included!
Learn more about the implications, comparative analysis with other tech giants, and consumer reactions to this controversial AI tool….
AI’s Contribution to Global Healthcare Developments
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of modern technology, revolutionizing various sectors and reshaping how we perceive and interact…
CleanMyMac X vs Malwarebytes
CleanMyMac vs Malwarebytes: Comparing Malware and Virus Removal Tools for Apple Applications…
Practical Steps to Optimize Your Wi-Fi Network
Optimizing your home Wi-Fi network involves several actionable strategies to enhance performance across various devices, including laptops, desktops, iPads, and tablets. Start by updating your router firmware to ensure you have the latest features and security improvements. Most modern routers have an easy-to-use interface that allows for automatic updates, which can significantly boost both speed and security.
Choosing the best router settings is crucial. Begin by selecting the optimal channel; many routers default to crowded channels, leading to interference. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to identify the least congested channel and switch your network accordingly. Security settings are equally important; WPA3 is currently the most secure option, but if your devices are not compatible, WPA2 is a suitable alternative.
Quality of Service (QoS) settings can prioritize traffic for specific applications or devices, which is particularly beneficial in households with multiple users. By allocating more bandwidth to streaming or gaming devices, you can ensure a smoother experience. Most routers offer user-friendly QoS settings in their management interface.
For extended coverage, consider using Wi-Fi extenders, mesh networks, or Powerline adapters. Wi-Fi extenders can help eliminate dead zones by amplifying the signal, while mesh networks offer a more seamless experience by creating a unified network with multiple access points. Powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring to extend your network, providing a reliable solution for areas with thick walls or other obstructions.
Device-specific optimization is equally important. Ensure that your devices have the latest drivers and software updates, as these can significantly impact connectivity and performance. Adjust device settings to favor Wi-Fi over cellular data, and disable background applications that consume bandwidth.
Finally, common troubleshooting steps can resolve many connectivity issues. Restarting your router and devices can often clear minor bugs. Additionally, periodically checking for interference from other electronic devices and ensuring your router is placed in a central, elevated location can maintain a stable and fast network.